Introduction to Quick Sort
Quick Sort is a divide-and-conquer sorting algorithm:
- Divide: Pick a pivot and split the array so items smaller than the pivot go to the left, items larger to the right.
- Conquer: Recursively sort both sides.
- Combine: Lists get merged as they are sorted in-place.
Why should you care?
- It’s fast (O(nlogn) average), used in real-world applications- system libraries, and teaches recursion/divide-and-conquer.
How Does Quick Sort Work?
Let’s see it step by step with this array:
Example Array:
44, 33, 11, 55, 77, 90, 40, 60, 99, 22, 88, 66
Step 1. Choose a Pivot
Let’s use the first element: 44.
Step 2. Partition
Rearrange so everything ≤44 is left, >44 is right.
- Which numbers will be on the left of 44 after partitioning?
- A) 33
- B) 90
- C) 22
- D) 77
(Answer: A and C)
After partitioning, the array might look like:
33, 11, 22, 40, 44, 90, 77, 60, 99, 55, 88, 66
Pivot 44 is now where it belongs.
Step 3. Recur on both sides
Apply the same process to the left and right sides.
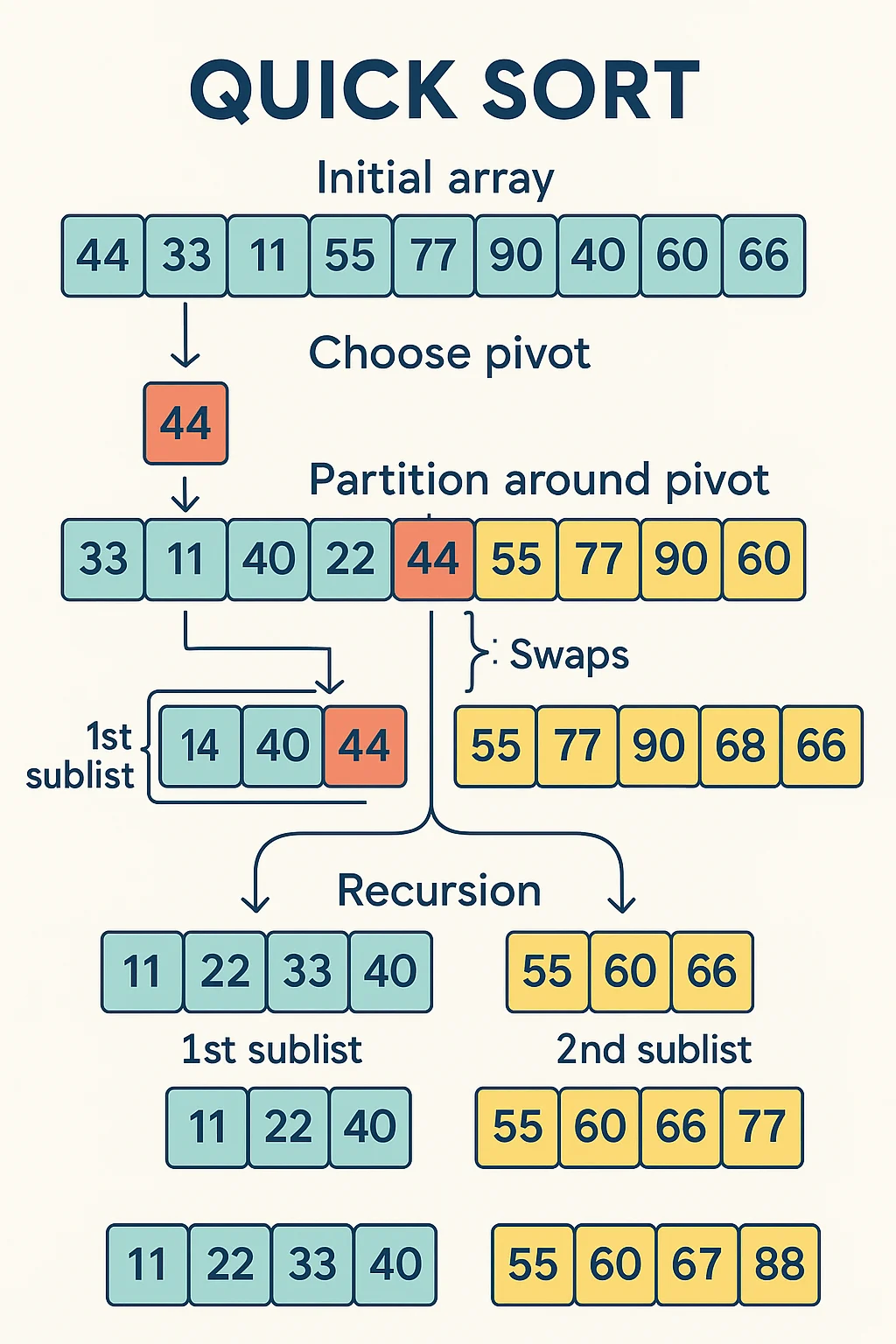
Can you trace what happens next?
Quick Sort Pseudo Code
procedure QuickSort(A, l, u) if l < u then k ← partition(A, l, u) QuickSort(A, l, k - 1) QuickSort(A, k + 1, u) end if end procedure procedure partition(A, l, u) pivot ← A[l] i ← l + 1 j ← u repeat while i ≤ u and A[i] ≤ pivot do i ← i + 1 end while while j ≥ l and A[j] > pivot do j ← j - 1 end while if i < j then swap A[i] and A[j] end if until i ≥ j swap A[l] and A[j] return j end procedure
Try tracing this with the sample numbers above!
Suppose the pick and swap process is:
44, 33, 11, 55, 77, 90, 40, 60, 99, 22, 88, 66
→
33, 11, 22, 40, 44, 90, 77, 60, 99, 55, 88, 66 (pivot 44 in correct spot)
Left subset: 33, 11, 22, 40
Right subset: 90, 77, 60, 99, 55, 88, 66
Keep applying quick sort recursively!
Interactive Quick Sort Demo
Sorted Output:
Analysis
Worst Case: O(n²) (when the pivot always leads to the most unbalanced split, e.g., already sorted data).
Best and Average Case: O(nlogn) (random pivots, or well-balanced splits).
Recurrence Relation (from notes):
- Worst: T(n) = T(n-1) + O(n)
- Average: T(n) ≤ 2T(n/2) + O(n)
Apply Master Theorem: Average is O(nlogn).
Space Complexity: O(log n) (recursion stack)
Quick Summary Table
| Case | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Stable? | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best/Average | O(nlogn) | O(logn) | No | Divide & Conquer |
| Worst | O(n²) | O(logn) | No | Divide & Conquer |
Try It Yourself: Self-Check
Given: 44, 33, 11, 55, 77, 90, 40, 60, 99, 22, 88, 66
- What’s the pivot on first pass?
- What’s the array after the pass?
- How does the process continue?
Real-World Applications
Quick sort is essential for:
- Sorting databases
- System libraries (C’s qsort, Python’s .sort uses Timsort—a hybrid which leverages quick sort ideas)
- Any large dataset that needs efficient, in-place sorting
Read more
Do Linked Lists still Matter? – tectrails.com
Top AI Courses to Elevate Your Career in 2025 – tectrails.com
